| Laws & Contracts > Contracts |
 Contracts
Contracts
Each PPP is unique and involves public and private partners. International institutions often participate to enhance the project's economic and financial feasibility. The contractual framework of a PPP infrastructure project involves a web of interdependent contractual relationships, organized around one main agreement.
This section assists in contract formation, drafting, implementation and management by considering contract formation (selection of contract type and procurement), selection of contract type, description of the significance of the most relevant contract clauses and other agreements, bonds and guarantees. Contract renegotiation and adaptation reviews the causes leading to renegotiation and the conditions for its success.
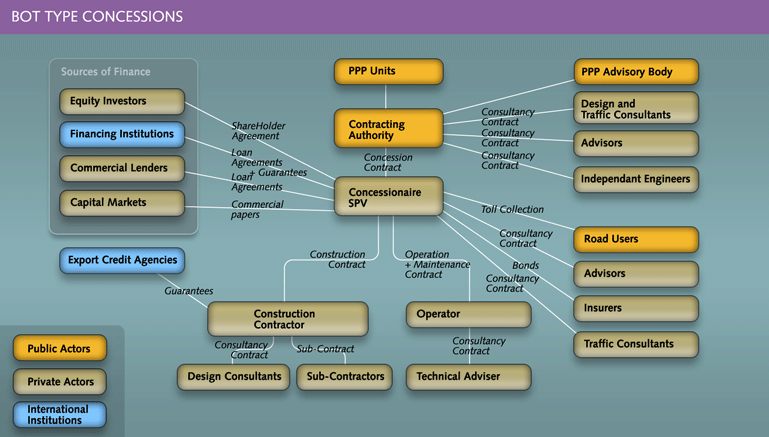
The contractual arrangements are described hereafter under the three principal PPP categories (Module 1 Main types of PPP) and as per the organization charts for PPP (Module 1 Actors and roles).
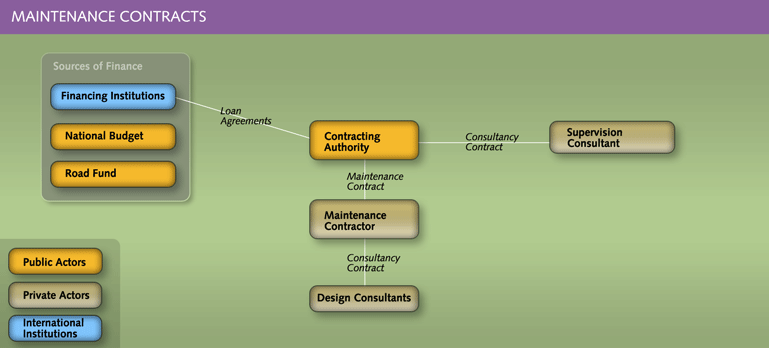
- Maintenance contracts are for projects involving a simple structure in which a Contractor signs a contract with a government institution (the Contracting authority). This relates particularly to performance-based maintenance contracts.
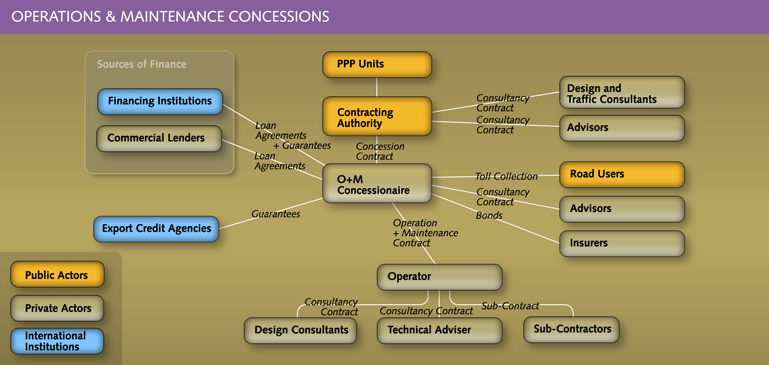
- Operation and maintenance concessions involve a more sophisticated organizational structure and sometimes require setting up a special purpose company run by the contractors to provide operation and maintenance services. These are also referred to as lease, franchise or affermage (brownfield) concessions.
- BOT type concessions. This organization chart represents the typical structure for those PPP projects, notably BOT, DBFO, BOO type (greenfield), in which:
- construction or major upgrading, operation and maintenance of the road are included in the scope of work
- private financing is mobilized in the form of project finance and,
- a special purpose company is set up for risk allocation and management purposes