| Tools > Case Studies | Types of PPP |
 Performance Based Contracts (PBC) in Serbia
Performance Based Contracts (PBC) in Serbia
WHY READ THIS CASE STUDY?
|
Background
In 2004 the International development Association (IDA) allocated credit amounts to the Republic of Serbia (then Serbia and Montenegro) for institutional capacity strengthening of PERS and for enhancement of road rehabilitation and maintenance, project known as the Transport Rehabilitation Project (TRP).
The World Bank project included the implementation of two pilot contracts involving routine maintenance of about 1200km of road in Mačva and Kolubara district, for 3 years. The rehabilitation part included ten road sections totalling about 240km.
Later the Swedish International Development Association (SIDA) donated an additional amount for consulting services related to winter maintenance, road safety and environmental protection issues.
The TRP was to be implemented over the four year period 2004 – 2008.
Project Description
The location of the pilot projects are illustrated in the following figures (Source: Routine and Winter Road Maintenance in Mačva and Kolubara Districts - Output and Performance based Road Contracts (OPRC) - presentation of 3 October 2006. The Highway Institute).
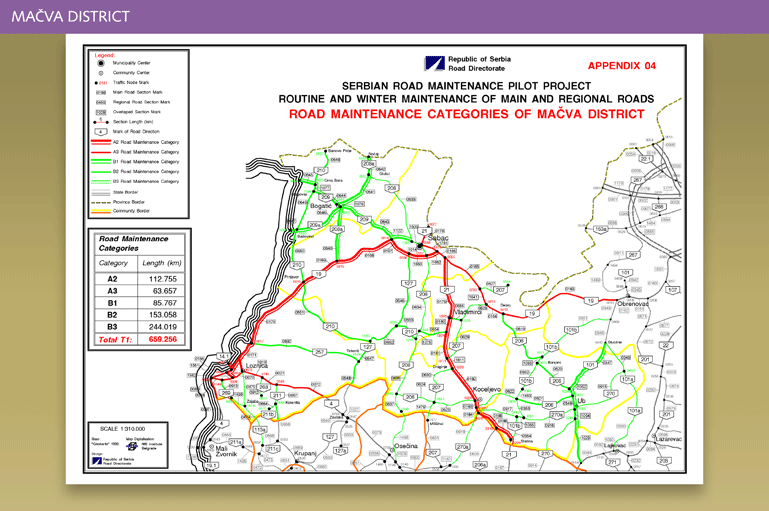
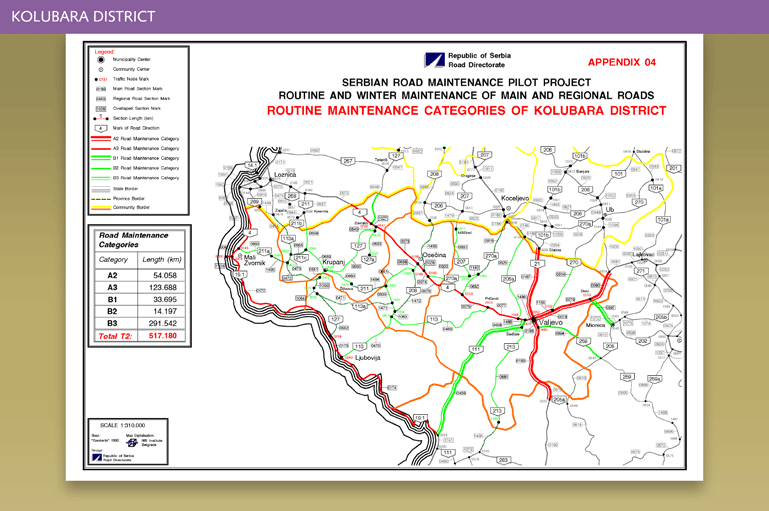
Details on the routine maintenance contracts are summarised below:
| Item | Mačva district | Kolubara district |
| Contract ID number | WBC/RMC/2003-1 | WBC/RMC/2003-2 |
| Scope | Routine maintenance works involving about 660 km of main and regional road network. The duties include administrative ones, routine road maintenance, routine bridge maintenance and winter road maintenance. | Routine maintenance works involving about 517 km of main and regional road network. The duties include administrative ones, routine road maintenance, routine bridge maintenance and winter road maintenance. |
| Cost estimate | 5.9 million USD | 5.8 million USD |
| Contract period | 4 years (2004 – 2008) | 4 years (2004 – 2008) |
| Contractor | Alpine Mayreder Bau GMBH | PZP Beograd |
In 2007, the total estimated cost for the performance based road maintenance was amended to 14.6 million USD, of which 13.1 million USD IBRD loan and the remainder government financing. The project will finance extending the ongoing PBC for 3 more years to include more routine maintenance activities, as an output rather than input basis.
Initially the rehabilitation part included ten road sections, as follows:
| Road | Section | Length (km) | Contract ID number |
| M-23 | Kragujevac - Ravni Gaj | 10.3 | WBC/RRC/2005-01 |
| M-23.1 | Ravni Gaj - Kraljevo | 33.9 | WBC/RRC/2005-02 |
| M-19 | Šabac - Zminjak | 20.9 | WBC/RRC/2005-03 |
| M-19 | Prnjavor - Loznica | 18.8 | WBC/RRC/2005-04 |
| M-21 | Šabac - Koceljeva | 34.0 | WBC/RRC/2005-05 |
| M-21 | Koceljeva - Valjevo | 27.8 | WBC/RRC/2005-06 |
| M-4 | Loznica - Zavlaka | 25.6 | WBC/RRC/2006-02 |
| M-4 | Zavlaka - Pričevići | 31.7 | WBC/RRC/2006-03 |
| M-4 | Pričevići - Valjevo | 12.4 | WBC/RRC/2006-04 |
| M-4 | Valjevo - Ćelije | 20.9 | WBC/RRC/2006-01 |
In addition, consulting services were sought for the supervision of works and environmental monitoring. The cost for this component was 1.6 million USD awarded to the Highway Institute (Institut Za Puteve a.d.), Belgrade, Serbia.
The total cost of the TRP was estimated at 61.3 million USD, of which 55 million USD were financed by the World Bank and 6.3 million USD by PERS. The rehabilitation works consumed most of the budget. In 2007 the total rehabilitation component was estimated to cost 36.2 million USD (of which 32.6 million USD IBRD loan). The project will finance approximately an additional 100km of roads, over and above the one listed above, as follows:
| M25 | Prokuplje – Mala Plana | 8.3km |
| M3 | Odzaci – Kula | 23.5km |
| M23 | Medjuluzje – Krevac | 10.4km |
| M4 | Krcevac – Topola | 2.6km |
| M5 | Marcovica – Ovcar Banja | 11.0km |
| M7 | Kac – Za Zabalj | 13.3km |
| R100 | Kruzni Put – Grocka – Smederevo | 31.9km |
Particular characteristics of the PBC
The road maintenance contracts were set-up according to an organised system which details the roles of the different role players, the works to be done and the associated monitoring of performance.
The consultant in charge of the works supervision and monitoring has an important role to play, as the liaison between the government and the contractors.
The consultant was assigned duties related to:
- routine road maintenance supervision
- bridge maintenance supervision
- preparation of road databases
- carrying out joint inspections with the contractors
- inspection and analysis reports.
Particular features include:
i. Environmental monitoring
Environmental monitoring entails the control using a check-list to sample, measure and report on pollution related matters, e.g. disposal of waste material, removal of wild deposit sites within the road reserve, adequate handling of fuel and lubricants, noise and vibrations during working hours, workers' safety.
ii. Winter road maintenance
Road maintenance works were classified by road classification (e.g. main highways with traffic above 6000 vpd, regional roads with traffic ranging between 3000 and 6000 vpd and so forth down to roads of below 500 vpd).
Two basic winter service standards were determined: a snow-free and skid-free standard (applied to the highest category of road A) and snow covered roads (applied to a lower category - B roads).
Preconditions for winter road maintenance, includes:
- the existence of a winter service plan
- timely provision of machinery, equipment and materials for road maintenance
- posting of winter traffic signs
- operation of a road winter information system (RWIS), which includes a network of meteorological stations positioned along main routes.
iii. Use of penalties (demerit points)
In case the maintenance standards were found to be below those stipulated, a penalty of points system is applied, according to which a number of points are equivalent to a monetary value:
| Range of points | Penalty value of 1 point in dinars | Penalty value of 1 point in USD equivalent |
| 1 to 50 | 20 000 | 385 |
| 51 to 75 | 50 000 | 960 |
| 76 to 125 | 100 000 | 1 920 |
| 126 to 175 | 120 000 | 2 310 |
| 176 to 200 | 150 000 | 2 880 |
| Above 200 | 200 000 | 3 840 |
Associated terms were determined which allow the employer to terminate the contract, e.g. if in the first year the contractor accumulates over 100 demerit points, if in the second year the contractor accumulates over 160 demerit points, etc.
iv. Traffic safety aspects
A road safety improvement component was introduced to support road safety improvement activities, including actual elimination of dangerous spots and road safety audits along the rehabilitated and maintained road sections in order to reduce and monitor accident trends. The estimated cost for this component was 2.1 million USD (of which 1.8 million USD IBRD loan).
Experience during various phases of the project
Rehabilitation works
Works are carried out within the existing right-of-way, avoiding any encroachments into potentially environmentally or cultural protected areas.
Interviews of drivers
Drivers were interviewed to express their views on the ongoing maintenance and road safety issues. The responses were not conclusive, as some drivers were satisfied with some items of the maintenance, while others complained about other items, such as, lack of shoulders, safety barriers or parking areas.
Control supervision by Consultants
Joint inspections by the supervision consultants and the maintenance contractors, the summaries of which were done using predetermined verification reporting formats, e.g. for road and bridge maintenance works, lead to unambiguous quantification of the works carried out. Results can therefore be measured and if need be, demerit points applied if works do not comply with the predetermined standards.
Conclusions and lessons learned
Setting up a PBC system, whereby the responsibilities of the contractors are clearly identified and controlled by specially appointed consultants, are likely to yield satisfactory results.
During the ongoing contract period improvements were noticed, notably with respect to:
- road conditions compared with the period prior to the maintenance contracts
- reduction in materials used for road maintenance purposes
- reduction of costs and material for winter maintenance
- cost savings for items contracted in accordance with performance based principles.
Further information
Routine and Winter Road Maintenance in Mačva and Kolubara Districts - Output and Performance based Road Contracts (OPRC) - presentation of 3 October 2006. The Highway Institute)
http://www.putevi-srbije.co.yu/pdf/1/
Nenad_Djordjevic_Highway_Inst_Pilot_Project_Consulting_Services_for_supervision_of_works.ppt